Prenatal genetic disorders are a major concern for expectant parents. The detection of such disorders during pregnancy is crucial, as it allows for appropriate medical care to be given to the mother and the baby.
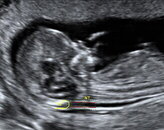
One of the key tests for detecting prenatal genetic disorders is the Nuchal Translucency (NT) test. NT is a non-invasive, ultrasound screening test that measures the thickness of the nape of the fetal neck. This test is usually carried out between the 11th and 13th+ weeks of pregnancy. The NT test is considered to be a reliable indicator of the risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down Syndrome in the unborn baby.
During the test, a trained healthcare professional will use an ultrasound machine to measure the thickness of the fluid-filled space behind the baby’s neck. If the thickness is thicker than normal, this can indicate a higher risk of Down Syndrome. In this case, the medical professional will recommend further tests to verify the diagnosis.
One of the advantages of the NT test is that it does not pose any risk to the mother or the baby. There are no needles, blood tests, or any other invasive procedures required for the test. Moreover, the test can also help to identify other potential health concerns such as structural defects, heart abnormalities or fetal infection. This makes the NT test an essential part of prenatal care.
Overall, the Nuchal Translucency test is a valuable tool in prenatal care that allows physicians to identify potential genetic disorders early in pregnancy
.